Heart Health Priority takes center stage with the release of the 2024 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines, marking a significant shift in the approach to managing elevated blood pressure and hypertension. These updated guidelines emphasize early intervention and lifestyle modifications, particularly targeting alcohol consumption and aiming for more aggressive blood pressure control to mitigate the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Table of Contents
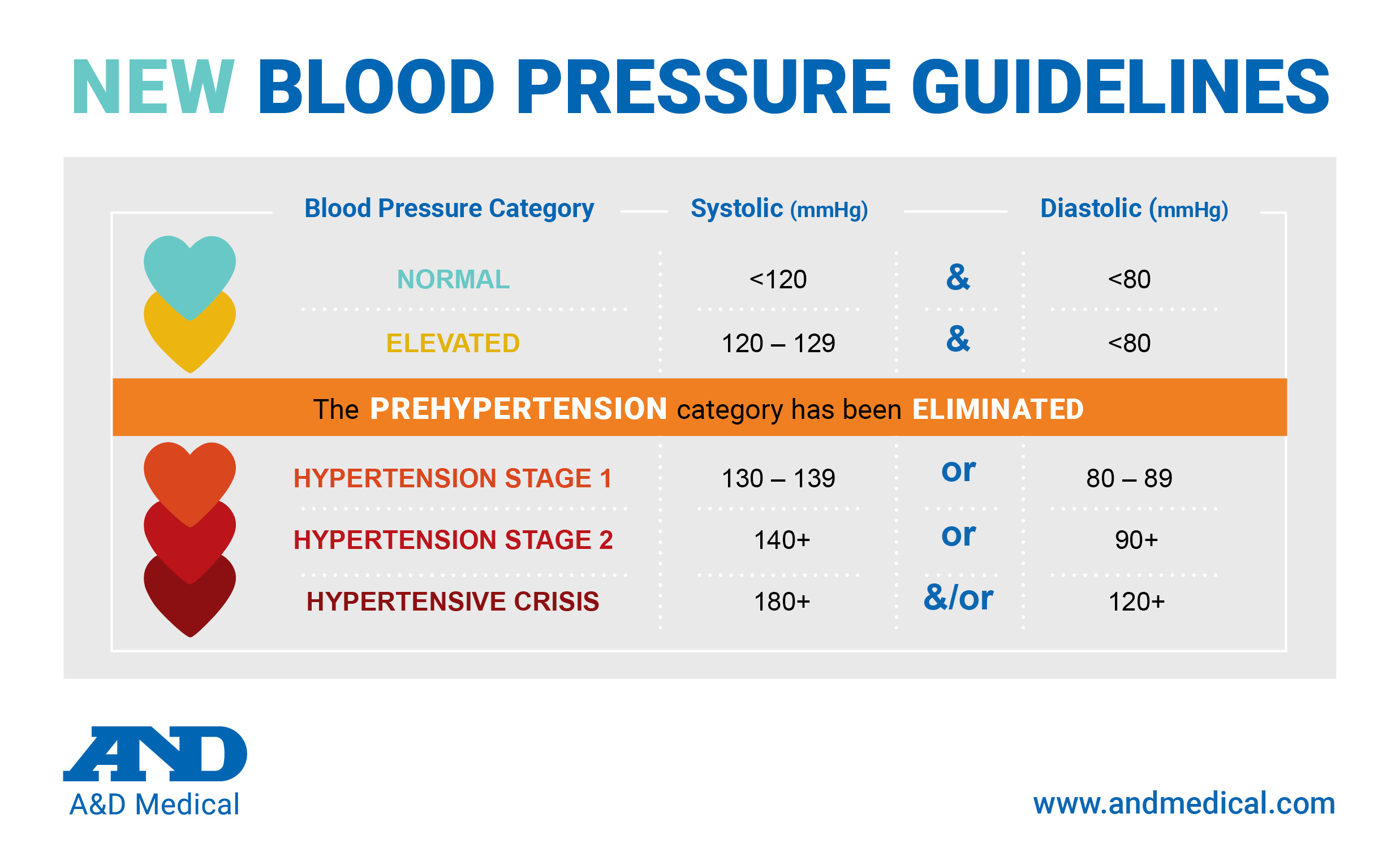
Understanding the New Blood Pressure Guidelines
The 2024 ESC Guidelines introduce a more proactive strategy for identifying and managing individuals at risk of cardiovascular diseases. These guidelines provide specific recommendations for blood pressure targets, lifestyle modifications, and early treatment, reflecting a comprehensive approach to heart health.
Aggressive Blood Pressure Targets
One of the most notable changes is the recommendation for a more aggressive systolic blood pressure (BP) target. The guidelines advise aiming for a systolic BP between 120-129 mmHg for most patients receiving BP-lowering medication, provided it is well tolerated. This lower target aims to reduce the strain on the cardiovascular system and decrease the likelihood of adverse events. This shift underscores the importance of personalized treatment plans, ensuring that blood pressure management aligns with individual patient needs and tolerances, as outlined by the ESC.
The New “Elevated BP” Category
The guidelines introduce a new category called “Elevated BP,” defined as a systolic BP between 120-139 mmHg or a diastolic BP between 70-89 mmHg. This categorization is designed to identify individuals at an earlier stage of risk, allowing for timely intervention before hypertension fully develops. The ESC emphasizes that this proactive identification can help prevent the progression to more severe cardiovascular conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications: A Cornerstone of Treatment
The 2024 ESC Guidelines place a strong emphasis on lifestyle modifications as the primary approach for all individuals with elevated BP and hypertension. These modifications include several key components, each playing a crucial role in managing blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health.
Dietary Changes
Adopting a healthy diet is paramount. The guidelines specifically recommend the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy, and whole grains, while being low in sodium, saturated fat, and cholesterol. This dietary pattern has been shown to significantly lower blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health. The ESC highlights the importance of nutritional education and support to help individuals adhere to these dietary recommendations.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is another critical component of lifestyle modification. The guidelines recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Regular physical activity helps lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and enhance overall cardiovascular fitness. The ESC suggests that healthcare providers should encourage patients to find enjoyable forms of exercise to promote long-term adherence.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing blood pressure. Overweight and obesity are significant risk factors for hypertension and cardiovascular disease. The guidelines recommend that individuals with elevated BP or hypertension aim to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of dietary changes and regular physical activity. The ESC emphasizes that even modest weight loss can have a significant impact on blood pressure and cardiovascular health.
Reducing Sodium Intake
Lowering sodium intake is a well-established strategy for managing blood pressure. The guidelines recommend limiting sodium intake to no more than 2.3 grams per day, and ideally even less. Reducing sodium intake can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. The ESC advises individuals to be mindful of hidden sources of sodium in processed foods and restaurant meals.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking is a major risk factor for hypertension and cardiovascular disease. The guidelines strongly recommend that individuals who smoke should quit. Smoking cessation can lead to significant improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular health. The ESC encourages healthcare providers to offer smoking cessation counseling and support to patients who smoke.
Alcohol and Blood Pressure: A Cautious Approach
The 2024 ESC Guidelines provide specific recommendations regarding alcohol consumption, reflecting a cautious approach to its potential impact on blood pressure and cardiovascular health.
Recommended Limits
The guidelines advise individuals to limit alcohol intake to no more than one standard drink per day for women and two for men. However, the ESC emphasizes that avoiding alcohol entirely is preferable for optimal health outcomes. This recommendation is based on evidence suggesting that even moderate alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure in some individuals.
The Case for Abstinence
The guidelines highlight that the safest approach for individuals concerned about their blood pressure is to abstain from alcohol altogether. The ESC notes that while some studies have suggested potential benefits of moderate alcohol consumption, the risks generally outweigh the benefits, particularly in the context of hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
Early Intervention: A Proactive Strategy
The 2024 ESC Guidelines prioritize early intervention, particularly for individuals at high risk of cardiovascular disease. This proactive strategy aims to prevent the progression of elevated BP to more severe hypertension and reduce the risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
High-Risk Individuals
For individuals with elevated BP and a high CVD risk (e.g., established CVD, diabetes, or a 10-year CVD risk of ≥10%), the guidelines recommend initiating lifestyle measures. If blood pressure remains ≥130/80 mmHg after three months, pharmacological BP-lowering treatment is recommended. This approach ensures that high-risk individuals receive timely and appropriate treatment to manage their blood pressure and reduce their risk of cardiovascular events, as stated by the ESC.
Prompt Treatment for Confirmed Hypertension
For all adults with confirmed hypertension (≥140/90 mmHg), the guidelines recommend prompt initiation of both lifestyle and pharmacological therapy, irrespective of age and CVD risk. This aggressive approach aims to quickly lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. The ESC emphasizes that early and effective treatment is crucial for improving long-term cardiovascular outcomes.
Conclusion
The 2024 European Society of Cardiology Guidelines represent a significant advancement in the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. By focusing on early intervention, aggressive blood pressure targets, and comprehensive lifestyle modifications, these guidelines offer a roadmap for reducing the burden of cardiovascular disease. The emphasis on limiting alcohol consumption and promptly addressing elevated BP underscores a proactive approach to Heart Health Priority, ultimately aiming to improve the cardiovascular health of individuals across Europe and beyond.
